The increasing availability and affordability of different products has contributed to improving the standard of living and quality of life. Yet, the current consumption system implies an overexploitation of all resources, generating an ever-increasing pressure on these resources that compromises their availability, and ultimately leads to a significant generation of waste. This is especially relevant in the food industry, as it plays a significant role in environmental degradation and climate change.
Therefore, the food industry needs to undergo changes to address these unsustainable level of consumption, and need to be based on a holistic transformation of the entire food chain based on the preservation of natural resources, more efficient production and distribution, the minimization of the impact on the environment, the reduction of the use of polluting materials, the fight against food waste, and the production of sustainable food.
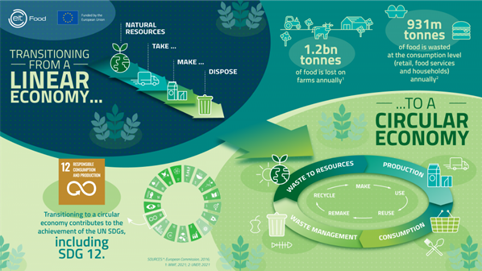
Transition from a linear to a circular economy.
The answer to the shift of the food industry towards sustainability lies in the structure of the economy. The traditional linear economy model follows a “take, make, use and dispose” system, in which products are used only once and then discarded, generating waste. In this context, the concept of circular economy arises: a production and consumption model based on the maximum use of resources with the aim of minimizing the impact on the environment.
The aim is to move from the traditional linear production model to a circular model in which the life cycle of the products are reconsidered from beginning to end (through reuse, recycling or recovery). The ultimate goal is to maintain the products in the production process the maximum time possible, thus avoiding the incorporation of new materials and minimizing the generation of non-usable waste.
In essence, it consists of adding value to the products, materials and resources used in the production process to maintain them economically productive the maximum time possible and generate the minimum amount of waste.
It is not about recycling anymore.
However, it is not enough to focus on packaging alone. Worldwide, food waste is extremely high. A 2021 report by WWF and supermarket Tesco analyzing on-farm food waste estimated that 2.5 billion tons of food is lost or wasted annually from production to consumption. More broadly, the FAO Food Loss Index (FLI) estimates that, globally, about 14% of all food produced is lost from the post-harvest stage to the retail stage ( FAO, 2019).
Looking specifically at the EU, about 88 million tons of food waste is generated annually. Out of this amount, it is estimated that 20% of the total food produced is lost or wasted, and 36.2 million people cannot afford a quality meal every other day ( Eurostat, 2020).
Renewed practices are therefore needed throughout the food chain, from those who produce and process food (farmers, food manufacturers and processors) to those who make it available for consumption (hospitality sector, retailers) and, ultimately, consumers. The last option is recycling, since the best waste is that which is not produced.
Circular economy in practice
In this context, and encouraged by technological advances, numerous organizations have been established to undertake actions to reduce waste in the food industry.
Too good to go

The company was born in 2016 with the aim of implementing a real change against food waste. Too good to goo is an app that connects establishments with daily food surpluses with users who are willing to consume them and prevent them from being wasted. The upside: companies reduce waste and consumers discover new places and save money.
For further information visit: https://toogoodtogo.es/
Feltwood
Feltwood is a company that develops technologies to produce eco-friendly industrial materials (fully biodegradable, recyclable and compostable), 100% vegetable fibers, from agricultural waste.
For further information visit: https://feltwood.com/

Orbisk
Orbisk aims to make the global food system more sustainable. Using innovative technology and artificial intelligence, its provides the food service industry with detailed information about their food waste. A smart camera on top of the garbage can, connected to a scale, automatically record all food that is thrown away down. This technology helps to reduce waste while optimizing the profit margin.
For further information visit: https://orbisk.com/en

Alchemic kitchen
The Alchemic Kitchen is an experimental development space that takes fresh food and surplus edibles in danger of being wasted and transforms them into new products. They work with local farmers, growers and food producers; support other social enterprises and cooperatives; and work with communities to develop new skills and employment opportunities.
For further information visit: https://www.alchemickitchen.org/

Interested in learning more? Visit:




